Business and Records Classifications Schemes (classification schemes) are a hierarchical set of terms for categorising an organisation's business information.
Once agreed upon, classifications schemes can be used to:
- Develop file titling conventions
You can use terms to develop file (container) titling conventions. - Streamline sentencing
You can map terms associated with records to disposal classes from records authorities. This can streamline and potentially automate sentencing using the disposal functionality in your recordkeeping system. -
Create enduring hierarchical structures
Classification schemes impose a hierarchical structure in a recordkeeping system.This helps your agency move away from an organisational information structure to a functions-based recordkeeping system, able to adjust for restructures and Machinery of Government changes.
- Standardise metadata and data entry
You can add terms as metadata tags or data-entry fields within a business system. - Help keep information secure
You can map security classifications to certain activities to auto-classify information. This means permission restrictions automatically apply to the information under that activity. For example, the activity 'security' may automatically apply a 'Protected' classification and restrict the information to named staff.
Hierarchical representation
Each classification scheme is traditionally represented as a hierarchy.
When used in a recordkeeping system, it can be a Records or File Plan. Each plan includes is a list of Functions and the Activities that fall under each function, as well as any topics or transactions that fall under each Activity. It may or may not have a scope note or definition for each term.
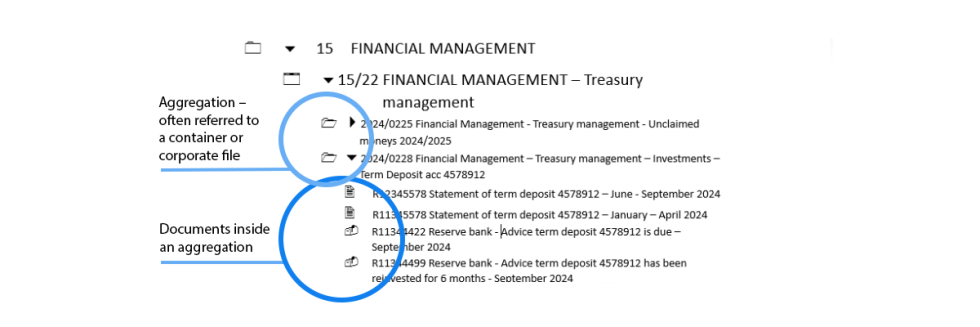
The example below is the functional term FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT and its associated activities and topics.
Financial Management
The function of managing an organisation's financial resources. This Includes: establishing, operating and maintaining accounting systems; controls and procedures; financial planning and analysis; framing budgets and budget submissions; obtaining grants; managing funds in the form of allocations from the Consolidated Revenue Fund and revenue from charging, trading and investments, and allocating and spending of funds to support the performance of agency functions
It also includes the monitoring and analysis of assets to assist the delivery of economic and social services to government, industry and the community.
- Accounting
The process of collecting, recording, classifying, summarising and analysing information on financial transactions, and subsequently on the financial position and operating results of the agency. Includes: financial statements and the implementation, maintenance, monitoring and auditing of the agency's accounting systems and internal controls. - Budgeting
The process of planning the use of expected income and expenditure over a specific time period. - Treasury management
The process of managing the funds of an agency in an efficient and economical manner by ensuring an effective system of internal control is on operation. Includes investments and loans.- Investments
Moneys put into an account or scheme to generate income. Note: When titling, add the name of the investment as free text. - Unclaimed moneys
Money that is owed to people or business but has not been claimed due to unshared changes to contact details. Note: When titling, add financial year.
- Investments
Often a Records Plan is used in an Electronic document and records management system (EDRMS) to structure records into a hierarchy that aids navigation.
Using the previous example, the EDRMS may look something like this: